IC Sensors
Introduction to Integrated Circuit Temperature Sensors
An
IC Temperature Sensor is a two terminal integrated circuit temperature transducer that produces an output current proportional
to absolute temperature. The sensor package is small with a low thermal mass and a fast response time. The most common temperature range is
55 to 150°C (-58 to 302°F). The solid state sensor output can be analog or digital.
OMEGA Engineering offers a wide range of
integrated circuit temperature sensors in Australia.
Learn more about IC Sensors
Typical IC Sensors Applications
1. Circuit boards: monitor and control temperature
2. Computers: control CPU temperature
3. Telecommunications: cell phones & PDAs™
4. Industrial immersion applications
Voltage Output IC Sensors
- Typically 10mV per degree C with nominal output correlated to 0K, 25°C.
- Some sensors have an offset at 0°C so that they can be used and read below 0°C without having to use a negative power supply.
- Non-linearity typically less than 1°C across their temperature range.
Current Output IC Sensors
- Nominal Output: 298 µA at 25°C
- 1 µA output per °C
Digital Output IC Sensors
- Have built in A-D Converters
- The number of digits in the A-D converter provides the resolution
- 10 Bit plus sign provides temperature resolved in increments of 0.25°C
- 12 Bit plus sign provides temperature resolved in increments of 0.0625°C
Where are IC Sensors used?
- On circuit boards to monitor and control temperature.
- In computers to control CPU temperature.
- In telecommunications applications (cell phones & PDA™).
- In some industrial immersion applications.
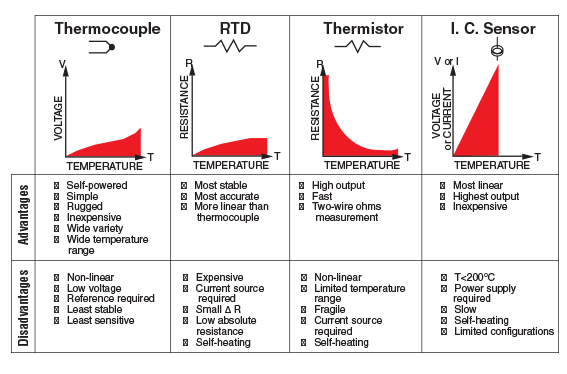
Strengths and Weaknesses of IC Sensors
Strengths:
- Analog or Digital outputs available
- Low cost
- Direct voltage, current or digital output needing no additional circuitry
- Linear output, no curve fitting
- Direct reading of temperature (1.000 = 100C and 298µA = 298K or 25°C) on some analog devices
- Various communication interfaces
Weaknesses:
- Narrow temperature range: -55 to 150°C Max
- Wider interchangeability than most RTDs and thermistors
- Wide variation in accuracy between different models
- Small package sizes can be a barrier to low cost applications in some immersion designs
Choose the right IC Sensor for your application
 Immersion IC Sensors
Immersion IC Sensors
An IC temperature probe consists of solid state sensor
housed inside a metallic tube. The wall of the tube is referred to as the sheath of the probe. A common sheath material is stainless steel.
The probe can come with or without a thread. Common applications are automotive/industrial engine oil temperature measurement, air intake
temperature, HVAC, system and appliance temperature monitoring.
 Transducer Type IC Sensors
Transducer Type IC Sensors
The IC transducer is small with a low thermal mass
and a fast response time. Ideally suited for applications such as: circuit boards to monitor and control temperature, computers to
control CPU temperature and telecommunications applications (cell phones).
Frequently Asked Questions
Why use IC Sensors in place of other technologies like Thermocouples, RTDs and Thermistors?
The analog IC solid state sensors provide an output as a voltage or current that is proportional with temperature without additional
circuitry. The digital IC sensors provide an output that has been processed thru an integral A-D converter and is ready for input into
digital control and monitoring systems. The IC sensors do not require linearization or other circuitry. The cost of IC sensors are also
very competitive with, in some cases less costly than, RTD and thermistor sensors
Shop for Integrated Circuit Temperature Sensors in Australia
The OMEGA Engineering Singapore office handles all inquiries and orders for Australia. We have Application Engineers and Sale Support Staff ready to assist you with your technical questions, quotations and orders. A one-stop source for process measurement and control, OMEGA provides support through web chat, e-mail and telephone. View our
contact page to call or email us.
Sensors | Related Products
↓ View this page in another language or region ↓
 Immersion IC Sensors
Immersion IC Sensors
 Transducer Type IC Sensors
Transducer Type IC Sensors

